Introduction
Student feedback plays a crucial role in the educational process. When delivered effectively, it allows students to recognize their strengths and areas for improvement. It not only highlights their achievements, but also guides them toward growth. By appreciating the value of student feedback and employing effective feedback techniques, educators can enhance the learning experience. This creates an environment where students feel empowered and achieve their highest potential.
Key Highlights
- Effective feedback is crucial for enhancing the learning process and boosting student performance.
- This blog explores the impact of feedback, different types of feedback, and strategies for delivering it effectively.
- Discover how personalized feedback and technology can be leveraged to maximize student learning.
- It also addresses the challenges of providing feedback, such as navigating negative feedback and ensuring timeliness.
- Lastly, the blog emphasizes the importance of measuring the impact of feedback and using it for continuous improvement in education.
Understanding the Impact of Feedback For Student Learning
Constructive feedback from the University of Texas plays a crucial role in enhancing student performance and fostering a positive learning environment. It highlights students’ strengths, as well as areas needing improvement. When students can identify where they can grow, they are more inclined to take charge of their own education and strive for better results.
Additionally, feedback helps students develop critical thinking abilities and deepen their grasp of the subjects they are studying. By providing clear and helpful advice, effective feedback enables students to better understand their learning goals.
Exploring the Role of Feedback in the Learning Process
Feedback serves as a guiding compass for students, directing them toward their learning objectives. Formative feedback takes place throughout the learning journey, while summative feedback is provided at the conclusion of a learning unit. This feedback allows students to adapt their learning strategies and deepen their comprehension as they progress. It’s an invaluable tool that enables quick adjustments and reinforces their understanding of key concepts at critical moments.
Additionally, feedback plays a crucial role in fostering metacognitive skills, encouraging students to reflect on their learning processes. They can identify their strengths and areas needing improvement. This self-awareness is vital for cultivating a growth mindset, empowering students to tackle challenges and view mistakes as valuable opportunities for growth.
Incorporating regular feedback into the learning experience generates a cycle of continuous improvement, empowering students to take an active role in their educational journey.
The Psychological Effects of Feedback on Students
The impact of feedback on students’ minds can significantly shape their motivation and engagement levels. When feedback is positive, genuine, and straightforward, it boosts students’ confidence and fosters a strong connection to learning. By acknowledging their efforts and celebrating their successes, teachers can instill pride in students, motivating them to strive for even greater achievements.
However, it’s essential to strike a balance between encouraging and constructive criticism. Feedback should promote growth without causing frustration. When giving constructive advice, pinpoint specific areas for improvement and provide practical suggestions, rather than simply highlighting mistakes.
Ultimately, the goal of feedback is to cultivate a supportive learning environment. This approach empowers students to embrace challenges, learn from their missteps, and achieve their full potential.
Encourage Continuous Feedback from Students
Encourage regular feedback from students is essential for developing a dynamic and adaptable learning environment that caters to their needs. This continuous exchange not only fosters open dialogue, but also empowers students to share their opinions on teaching strategies and learning resources. By consistently gathering input through surveys, suggestion boxes, or guided discussions, teachers can gain valuable insights into how students feel and experience. This approach helps pinpoint areas that might require changes, and reinforces the idea that student input is important in education. Moreover, nurturing a culture of reciprocated feedback motivates students to take charge of their learning journey. They begin to value the feedback they receive and feel inspired to share their thoughts to improve classroom interactions. By acting on student feedback, educators foster a collaborative relationship that encourages ongoing enhancement of the learning experience for everyone involved.
Types of Feedback and Their Effectiveness
Feedback comes in various forms, each with unique advantages and considerations to keep in mind. Understanding these different types enables teachers to blend their approaches and select the most suitable one for specific situations or educational objectives, always considering the assignment’s intentions. Tailoring feedback to align with the context and individual needs of students is crucial to be effective.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore several types of feedback. We’ll look at their characteristics and examine how they influence student learning.
Positive vs. Constructive Feedback: A Comparative Analysis
Positive feedback and constructive feedback are two fundamental types of feedback, each playing a distinct role in student learning. While positive feedback aims to reinforce desired behaviors and attitudes, constructive feedback focuses on identifying areas for improvement and providing further clarification and guidance for growth.
| Types of Feedback | Purpose | Example |
| Positive Feedback | To reinforce positive behavior and build confidence. | “Excellent work on your essay! Your arguments were well-structured and supported by strong evidence.” |
| Constructive Feedback | To identify areas for improvement and provide guidance for growth. | “Your essay shows good understanding of the topic, but the conclusion could be strengthened by summarizing the key arguments more concisely.” |
Effectively utilizing both types of feedback helps create a balanced and supportive learning environment. Educators must recognize the importance of acknowledging and strengthening positive progress, while also providing specific and actionable guidance for improvement.
Immediate vs. Delayed Feedback and Student Performance
The timing of feedback plays a significant role in student performance. When feedback is provided immediately after an activity, it enables students to identify and correct errors, enhancing their comprehension. This approach is particularly beneficial for tasks that require immediate application of their knowledge.
On the other hand, feedback after a delay can be more appropriate for larger projects or assessments. This allows teachers to offer more comprehensive insights and support, addressing a wide range of skills and concepts, as students have had the chance to reflect on their work.
Ultimately, the choice between immediate and delayed feedback should be based on learners’ needs, the complexity of the task, and the specific learning objectives in mind.
Strategies for Delivering Effective Feedback
Giving effective feedback requires careful thought and a focus on the student. Teachers should use methods that make everything clear, encourage thinking, and support a growth mindset. When teachers use these methods, they can create a feedback process that truly matters and helps every student.
The next sections look at practical strategies teachers can use to improve their feedback practices. This will help students take ownership of their learning journey.
Creating Actionable Feedback for Students
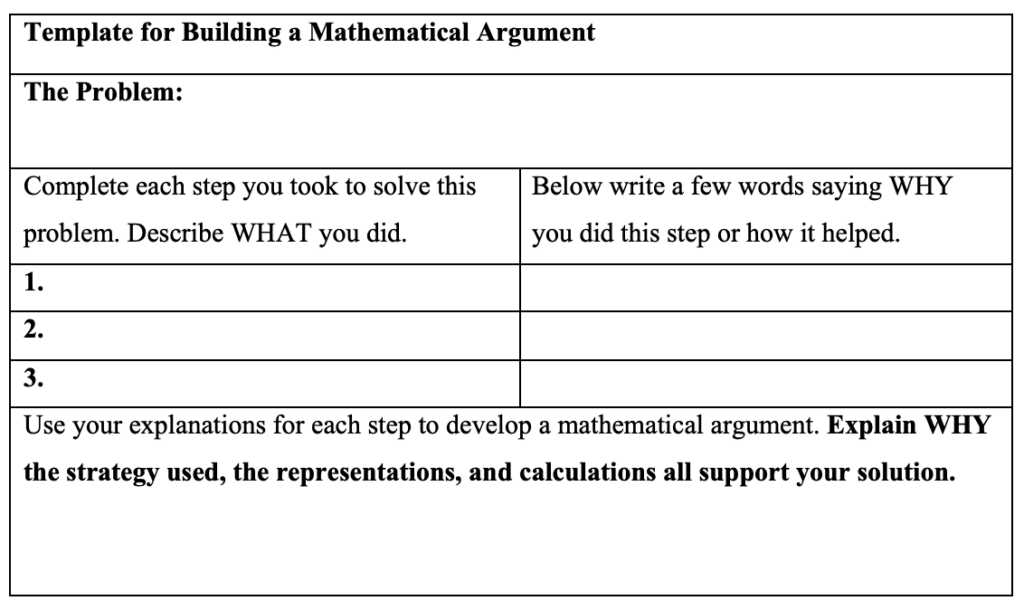
Creating actionable feedback for students is essential for fostering a learning environment where growth and improvement are prioritized. Actionable feedback goes beyond mere praise or criticism; it provides clear, specific, and targeted suggestions tailored to each student’s needs. To ensure feedback is effective, teachers should focus on the steps students can take to enhance their understanding or performance in a given task. Utilizing examples from a student’s work can illustrate the points made, making it easier for them to recognize how to apply the suggested changes in future assignments. Moreover, empowering students to reflect on their feedback fosters independence and critical thinking, enabling them to set personal goals for improvement. By making feedback actionable, educators not only enhance students’ skills, but also help them develop a proactive approach to their learning journey, cultivating an atmosphere that values continuous growth and self-improvement.
Creating a Culture of Feedback
Creating a culture of feedback is essential for fostering a supportive and growth-oriented learning environment. When students and educators prioritize feedback, it transforms the educational landscape into a collaborative space where learning is continuous and evolving. This culture encourages open dialogue, allowing students to feel safe to express their thoughts and concerns without fear of judgment. Teachers should model constructive feedback practices, demonstrating how to give and receive feedback effectively, which lays the groundwork for students to engage in meaningful peer reviews. Furthermore, integrating feedback into daily routines—through discussions, reflections, and regular check-ins—reinforces its importance and normalizes the practice. By emphasizing the value of feedback, educators cultivate a mindset of improvement, where both students and teachers see challenges as opportunities for growth, paving the way for enhanced learning outcomes and deeper engagement in the educational process.
Partnering with Students for Feedback
Partnering with students for feedback creates a dynamic learning environment where both educators and learners collaborate to enhance the educational experience. By involving students in the feedback process, educators cultivate ownership and accountability over their learning. This partnership allows students to share their insights and perspectives, which can lead to more tailored and effective feedback. Additionally, it encourages students to take an active role in their evaluation, as they become more aware of their strengths and areas for growth. Workshops and structured discussions can facilitate this partnership, providing students with a platform to express their thoughts and suggest improvements. By fostering this two-way dialogue, educators can not only refine their feedback practices, but also empower students to become reflective practitioners, thus nurturing a continuous cycle of growth and improvement in learning outcomes.
Aligning Feedback with Learning Objectives
Aligning feedback with learning objectives is crucial to ensure that students understand what they have learned, but also why it matters. When feedback directly relates to specific learning goals, it provides students with a clear framework for evaluation and improvement. This connection helps students see the relevance of the feedback they receive, and motivates them to engage more deeply with the material. Educators can enhance this alignment by clearly communicating the objectives at the start of each lesson and consistently referring back to them during feedback sessions. For instance, when discussing a student’s work, teachers can highlight how certain aspects met or missed the established learning targets, offering precise suggestions for improvement tied directly to these objectives. This reinforces the purpose of their efforts and fosters a growth mindset, as students understand that feedback is not just a critique, but a valuable tool in their learning journey.
Utilizing Technology for Efficient Feedback Delivery
In today’s digital world, technology gives us many tools to help with feedback in higher education. These tools make the feedback process easier and save teachers time. They also improve the quality and effect of the feedback. Using learning management systems or interactive platforms, teachers can provide timely and focused feedback that meets different learning styles.
For example, platforms that support audio or video feedback create a more personal and fun experience for students. Tools that allow real-time feedback during online activities help students understand and correct mistakes immediately, which can be especially beneficial in larger classes. Teachers can also use online rubrics and assessment tools for clear and regular feedback on assignments.
By using technology wisely, teachers can give feedback that boosts student learning and creates a more engaging classroom experience.
Incorporating Peer Feedback for Enhanced Learning
Peer feedback is a helpful way to improve learning. It allows students to learn from each other. They also get different viewpoints on their work. When students participate in peer feedback, they build critical thinking skills. They also strengthen their communication skills. This helps them understand learning objectives better.
Here’s how peer feedback improves the learning experience:
- Multiple Perspectives: Students get ideas from their peers. This helps them see more about the topic and find areas to work on that they might have missed.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Giving and receiving feedback in a friendly way teaches important communication skills.
- Increased Engagement and Ownership: Peer feedback makes learning more active. It encourages students to take ownership of their learning by sharing and using constructive tips.
By adding peer feedback to the lessons, teachers create a teamwork-focused environment. This helps both students give feedback and those receiving it.
Challenges in Providing Feedback and How to Overcome Them
Giving good feedback can be hard. Teachers often deal with issues like not having enough time, handling negative feedback, and making sure students understand and use the useful feedback. These problems can make feedback less effective and slow student progress.
Still, if teachers recognize these challenges and use plans to fix them, they can build a system for feedback that works better and helps both them and their students.
Navigating the Pitfalls of Negative Feedback
While feedback helps students grow, negative feedback can hurt them if it’s not given carefully. This can lower their motivation and self-esteem. When you criticize a student’s work without clear ways to improve, it can be discouraging.
To avoid negative feedback problems, try to give it in a positive way next time. Focus on chances for improvement, not just mistakes. Instead of saying, “This is wrong,” you could say, “I see where you’re going, but consider this approach.” Give clear examples and specific steps. This way, you help the student see how to improve and feel confident in doing it.
Always remember, feedback should guide and encourage students, not bring them down. When you handle negative feedback with care and focus on solutions, you help students build a growth mindset. This empowers them to face challenges better.
Ensuring Timeliness and Relevance in Feedback Provision
Timeliness and relevance are important for good feedback. When feedback is given a long time after a task is done, it loses its value. Students might have moved on or forgotten details about their work. Quick feedback helps students think about it and use it for future tasks.
Make sure your feedback is related to the learning objectives and the standards for the task. Avoid general comments that don’t give clear insights or point out specific areas to improve. Focusing on a few key parts helps students work better and see real progress, making their learning experience more positive and productive.
By giving timely and relevant feedback, teachers show they care about their students’ progress, and that the feedback is meant to help them grow and understand better.
Measuring the Impact of Feedback on Student Achievement
Measuring how feedback affects students is important for teachers. This helps them figure out if their feedback works and if they need to change it. By looking at how students react to feedback and using that information in future lessons, teachers show they care about the students and want to keep improving.
Using different tools, like quizzes, surveys, and self-reviews, can give helpful ideas on how students grasp and use the features of effective feedback given. Teachers can then check this information to find trends and spots where they might need to improve their feedback methods.
Tools and Techniques for Assessing Feedback Effectiveness
A range of tools and methods can be used to check how feedback helps students learn. These methods do more than just collect student work after giving feedback. They promote thinking, discussion, and real use of the feedback received.
One common way is to use exit tickets at the end of a lesson or unit. In this, students write down what they have learned and how the feedback helped them understand better. Another way is to encourage self-reflection. Students can use journals or online platforms to share the learning process and talk directly about the feedback.
By using these assessments, teachers can understand how their feedback makes a difference. They can adjust their teaching style to meet the different needs of their students. This ongoing process keeps feedback as a strong tool for learning and growth.
Feedback as a Tool for Continuous Improvement in Education
In the changing world of education, it’s important to keep improving. Quality feedback is key in this process. When teachers embrace a culture of feedback, they show they want to give their students the best learning experience.
This means teachers should stay open to student feedback about teaching methods, course content, and tests. Using student suggestions can help make learning more engaging and effective. Teachers should also seek feedback from their colleagues and participate in professional development that centers around feedback. This can give them useful insights and help them improve their teaching practices.
In the end, using feedback to keep improving helps both teachers and students. It creates a lively and responsive educational environment.
Reflecting on Your Feedback Practices as an Educator
As teachers, it’s important to think about how we give feedback. This helps us support our students better. We need to look at our methods often. We should be open to new ideas and remember that giving good feedback is something we keep working on.
Ask yourself: Is your feedback quick, clear, and helpful during office hours? Does it help students take charge of their learning and inspire them to get better? By looking closely at how we give feedback and finding ways to improve, we can create a better learning space for our students.
Conclusion
Student learning greatly benefits from effective feedback, as it enables educators to enhance the educational environment. Tailoring feedback, leveraging technology, and incorporating peer interactions are excellent strategies to keep students invested in their studies. It’s crucial to address challenges like negative feedback and ensure timely responses. This approach can significantly aid students in their academic journeys. Additionally, continually refining feedback practices can lead to remarkable student accomplishments. As educators, when we thoughtfully consider how to deliver feedback and experiment with new approaches, we enrich the learning experience. Let’s collaborate to ensure that feedback becomes a fundamental aspect of student success.
For Review