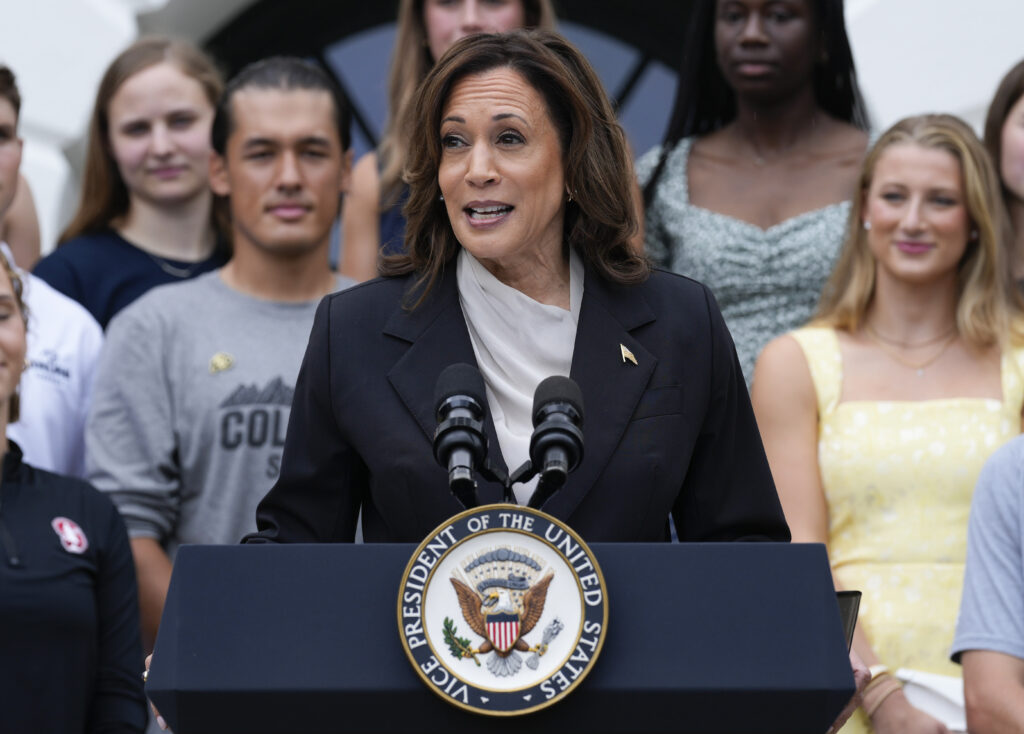
Vice President Kamala Harris speaks from the South Lawn of the White House in Washington on Monday during an event with NCAA college athletes. This is her first public appearance since President Joe Biden endorsed her to be the next presidential nominee of the Democratic Party.
Credit: AP Photo / Susan Walsh
The likelihood that Vice President Kamala Harris will be the Democratic nominee for president is inviting scrutiny of her positions on every public policy issue, including education.
By her own accounting, those views have been profoundly shaped by her experiences as a beneficiary of public education, as a student at Thousand Oaks Elementary School in Berkeley and later at the Hastings College of Law (now called UC Law San Francisco).
Just three months ago, in remarks about college student debt in Philadelphia, she paid tribute to her late first grade teacher Frances Wilson, who also attended her graduation from law school. “I wouldn’t be here except for the strength of our teachers, and of course, the family in which I was raised,” she said.
The most memorable moment in Harris’ unsuccessful 2019 campaign for president was in the first candidates’ debate when she sharply criticized then-Vice President Joe Biden for opposing school busing programs in the 1970s and 1980s.
“There was a little girl in California who was part of the second class to integrate her public schools, and she was bused to school every day, and that little girl was me,” Harris said in the debate.
She was referring to Berkeley’s voluntary busing program set up in 1968, the first such voluntary program in a sizable city. Biden was apparently able to put the exchange aside when he selected her to be his running mate several months later.
At age 12, her family moved to Montreal where she attended a public high school, and then went to Howard University, the Historically Black College and University in Washington D.C. for her undergraduate education.
It is impossible to anticipate what if any of the positions Harris took earlier in her career, or as a presidential candidate five years ago, will be revived should she win the Democratic nomination, or even become president.
But they certainly offer clues as to positions she might take in either role.
When she kicked off her campaign for president at a boisterous rally in downtown Oakland in January 2019, she made access to education a major issue. “I am running to declare education is a fundamental right, and we will guarantee that right with universal pre-K and debt-free college,” she said, referring to pre-kindergarten.
By saying education is a fundamental right, Harris addressed directly an issue that has been a major obstacle for advocates trying to create a more equitable education system.
While education is a core function of government — even “perhaps the most important function,” as Chief Justice Earl Warren wrote in the 1954 Brown v. Board of Education ruling — it is not a right guaranteed by the U.S. Constitution. That has meant relying much more on state constitutions.
During her term as vice-president, she has played a prominent role in promoting a range of President Biden’s education programs, from cutting child care costs to student loan relief.
Last year she flew to Florida especially to take on Gov. Ron DeSantis over his attacks on what he dismissed as “woke indoctrination” in schools. In particular, she was incensed by the state’s middle school standards that argued that enslaved people “developed skills that could, in some instances, be applied for their personal benefit.”
DeSantis challenged her to debate him on the issue — an offer she scathingly rejected. “There is no roundtable, lecture, no invitation we will accept to debate an undeniable fact: There were no redeemable qualities to slavery,” she declared at a convention of Black missionary women in Orlando.
Earlier in her career, she was best known on the education front for her interest in combating school truancy — an interest that could be extremely relevant as schools in California and nationally grapple with a huge post-pandemic surge in chronic absenteeism.
Students are classified as chronically absent if they miss 10% or more of school days in the school year.
Nearly two decades ago, while district attorney in San Francisco, she launched a student attendance initiative focused on elementary school children. Each year, she sent letters to all parents advising them that truancy was against the law. Prosecutors from her office would meet with parents with chronically absent children. If they did not rectify the situation, they could be prosecuted in a special truancy court — and face a fine of up to $2,500 or a year in county jail.
By 2009, she said she had prosecuted about 20 parents. “Our groundbreaking strategy worked,” she wrote in an opinion piece in the San Francisco Chronicle, citing a 20% increase in attendance at the elementary level.
When she ran for California attorney general in 2010, she backed a bill that enacted a similar program into state law. The law also subjected parents to fines and imprisonment for up to a year, but only after they had been offered “support services” to address the pupil’s truancy.
This tough stance put her on the defensive when she ran for president, and she softened her position on the issue. She said the intent of the law was not to “criminalize” parents. And in her memoir “The Truths We Hold: An American Journey,” Harris described her approach to truancy as “trying to support parents, not punish them.”
As attorney-general, she used the clout of her office to go after for-profit colleges she accused of false and predatory advertising, and intentionally misrepresenting to students the benefits they could provide. She was able to get a $1 billion judgment against the California-based Corinthians Colleges Inc. which eventually declared bankruptcy. ““For years, Corinthian profited off the backs of poor people – now they have to pay,” she said at the time.
During her presidential campaign five years ago, she made a major issue of what she labeled “the teacher pay crisis.” She said as president she would increase the average teacher’s salary by $13,500 — representing an average 23% increase in base pay. Almost certainly the most ambitious proposal of its kind made by any presidential candidate, the cost to the federal government would be enormous: $315 billion over 10 years.
To pay for it, she proposed increasing the estate tax on the top 1% of taxpayers and eliminating loopholes that “let the very wealthiest, with estates worth multiple millions or billions of dollars, avoid paying their fair share,” she wrote in The Washington Post.
Also on the campaign trail, she proposed a massive increase in funding to historically Black colleges and universities — one of which (Howard University in Washington, D.C.) she graduated from. In fact, she proposed investing $2 trillion in these colleges, especially to train Black teachers. She contended that if a child has had two Black teachers before the end of third grade, they’re one-third more likely to go to college.
Biden was able to push through a big increase in support for such institutions totaling $19 billion — far short of her goal of $2 trillion.
Many of her positions on education — including a push for universal pre-school, and making college debt-free — were aligned with those proposed by Biden, or ultimately implemented by him as president.
For that reason, there is likely to be continuity in her candidacy with much of the education agenda proposed by Biden.
But mainly as a result of lack of action in Congress and Republican-initiated lawsuits blocking his proposals, many of the administrations’s aspirations, like making community colleges free, doubling the size of Pell Grants, and student debt refiled, remain unfulfilled.
It will now be up to Harris — and the American voter — whether she will have the opportunity to advance that unfinished education agenda.
This story has been updated to include details about Harris’ education after her parents moved from Berkeley to Canada when she was 12.