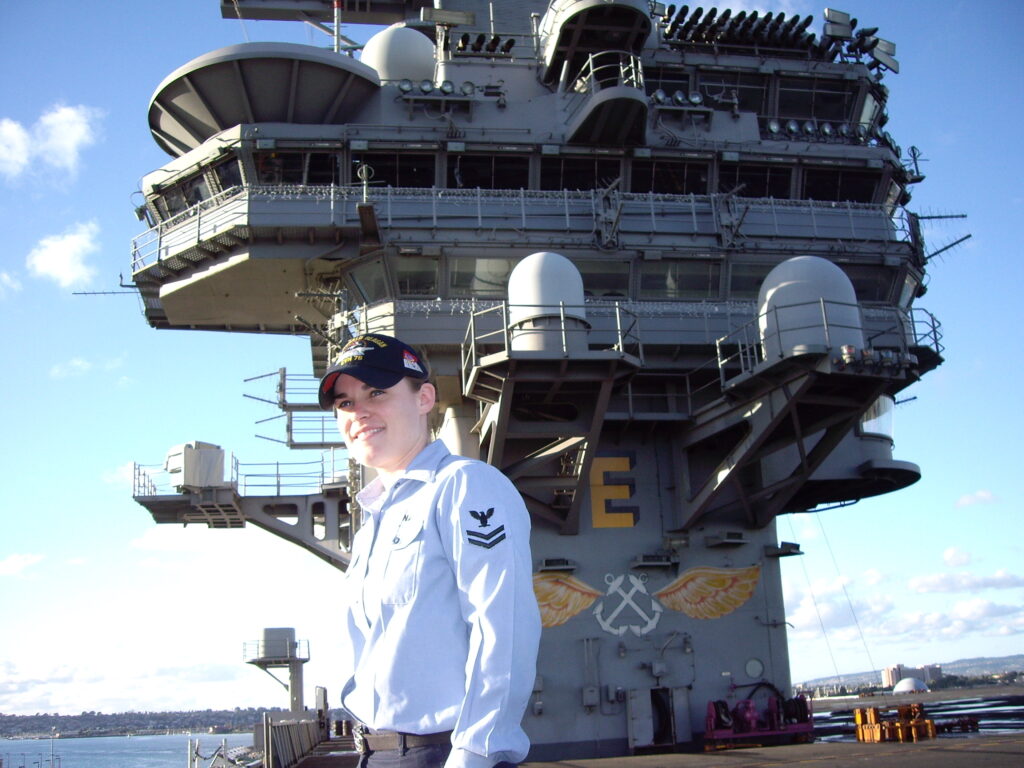
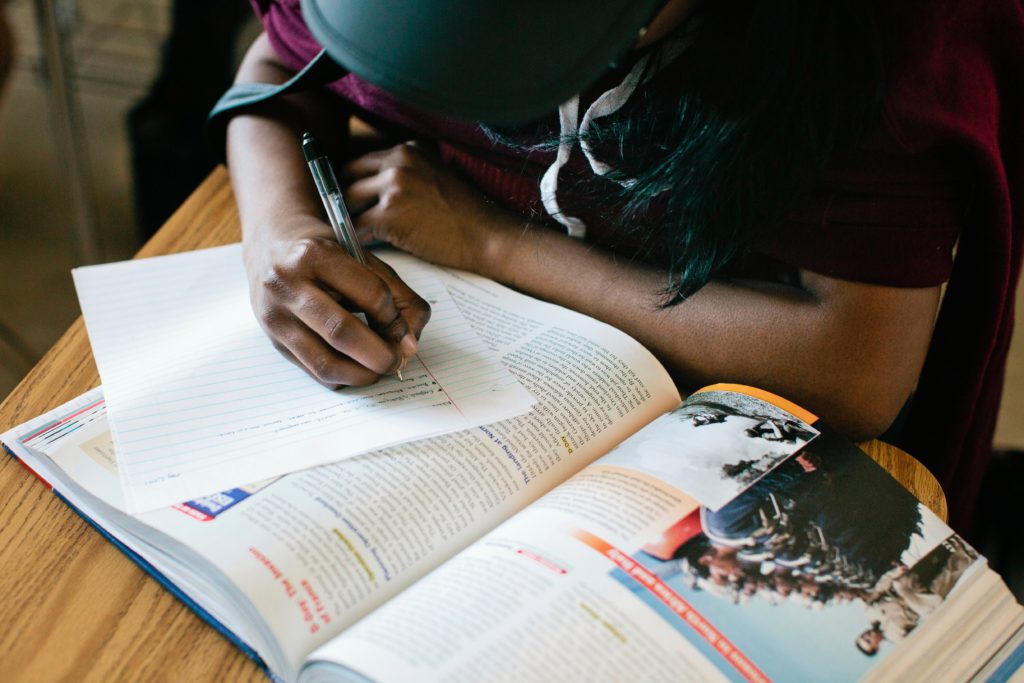
Kindergarten teacher Carla Randazzo watches a student write alphabet letters on a white board at Golden Empire Elementary School in Sacramento.
Credit: Rich Pedroncelli / AP Photo
California’s students have struggled in the five years since the pandemic closed schools across the state. But kids in many schools are bouncing back, returning to pre-Covid achievement levels. What’s working? How have some districts innovated to turn kids’ learning curves upward once again?
After analyzing student-level statewide data and visiting nine districts in each of the past three years, our team has made these discoveries:
Mindful policies make a difference
Nationwide, the pandemic erased nearly two decades of progress in math and reading. In California, average math proficiency decreased by 6.4 percentage points between 2019 and 2022, and reading proficiency dropped by 4 percentage points. Our work shows a modest positive effect of early reopening and federal recovery investments over this period. This highlights the importance of keeping schools open when it is safe to do so and prioritizing high-need students in reopening. Federal stimulus dollars also helped during this period.
Our statewide work further shows that districts blended, braided and sequenced multiple funding sources to extend instructional learning time, strengthen staffing and provide learning supports.
We also studied the impact of recovery investments and specific district recovery programs. We did not find that increased federal Covid funding to schools increased student test scores post-pandemic. However, districts that devoted funds to teacher retention efforts and extended learning time showed more improvement in student attendance, a key to improving academic outcomes.
Cross-sector partnerships advance whole-child development
Prolonged school closure, social isolation, economic anxiety, housing and food insecurity, Covid-19 infection, and the loss of loved ones exacerbated a national mental health crisis already underway before the pandemic. In 2021, 42% of high school students nationwide experienced persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness, and 32% attempted or seriously considered attempting suicide. As schools reopened, educators found themselves dealing with not just academic learning, but also support for basic needs (such as food and health care), mental health, and life skills (such as relationship skills).
Some districts pivoted to fostering whole-child development. For example, Compton Unified partnered with community health providers to offer health care services (such as vaccinations and check-ups), and Del Norte Unified leveraged Medi-Cal reimbursements to provide mental health counseling and therapy sessions. Educators will still need to deal with the academic, behavioral and life-skills needs for years to come. More cross-sector partnerships with public health, social services and housing would better equip schools to address these challenges.
School innovations foster a rebound in learning
Overall spending infusions have helped students rebound, but the impact has been relatively small. More important is how Covid relief funds were spent by districts. Our longitudinal case study of nine districts revealed some substantial organizational changes — reforms that may stick over time.
One large structural reform was the investment in student well-being. Before the pandemic, student well-being was considered mostly secondary to instruction and academic achievement. However, the pandemic highlighted the need to integrate life skills into instruction. As a result, districts invested in new program materials and moved resources to hire counselors, social workers, psychologists, and increased student access to school-based supports. Some even built new community centers where students and families come together.
A smaller scale, yet key, reform is districts’ investment in career pathways. Districts like Compton and Milpitas Unified offer a wide variety of pathways — from E-sports to computer science to early education — that are tied to on-the-job internships and certificates. These pathways have played an important role in engaging students and connecting them with employment opportunities.
Districts also tried new approaches to the structure of schooling and classroom practices. For example, Glendale Unified shifted to a seven-period block schedule that allowed middle and high school students to add an elective course that sparked their interest. In Poway Unified, small groups of students meet with teachers and classroom aides to focus on specific skill areas.
Digital innovations engage students, but gaps remain
Many districts have turned to digital innovations to motivate kids. In Poway, coaches embedded in the classroom work with teachers to build learning stations, where stronger students work in teams, freeing teachers to provide more direct instruction to kids at risk of falling behind.
Unfortunately, since the pandemic, the digital divide has narrowed, but it has not been eliminated.
In spring 2020, when schools abruptly shifted online, 40% of California households with school-age children did not have reliable internet or devices for distance learning. Over time, the state has made remarkable progress in device access, but not as much progress with internet access. The lack of progress could be attributed to multiple factors, including the absence of pre-existing infrastructure and affordability challenges. Federal and state governments provided unprecedented investments (such as the federal Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program and California Senate Bill 356) to address barriers to universal broadband access; however, communities face significant challenges in building out infrastructure and improving affordability.
The pandemic provided an unprecedented opportunity to rethink and restart public education. Given the increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters, learning disruptions will become the new norm for many communities throughout the U.S.
By learning from the example of districts that have demonstrated resilience and success in pandemic recovery, we can better prepare for future disruptions and build a more resilient public education that supports all students.
•••
Niu Gao is a principal researcher at the American Institutes for Research. Julian Betts is a professor at UC San Diego. Jonathan Isler and Piper Stanger are administrators at the California Department of Education.
Bruce Fuller, professor of education and public policy at UC Berkeley, was part of the research team and contributed to this report.
This collaboration research is supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through grant R305X230002 to the American Institutes for Research (AIR). Any errors or misinterpretations belong to the authors and do not reflect the views of the institute, the U.S. Department of Education or the California Department of Education.
The opinions expressed in this commentary represent those of the authors. EdSource welcomes commentaries representing diverse points of view. If you would like to submit a commentary, please review our guidelines and contact us.