Credit: Alison Yin / EdSource
Este artículo está disponible en Español. Léelo en español.
Long-term English learners who have been enrolled in U.S. schools for more than six years without becoming proficient in the language do worse on California’s math and English language arts tests than English learners who have been enrolled for fewer than six years.
California released data for the first time on long-term English learners’ achievement in standardized tests in math, English language arts and science for the 2022-23 school year, after a bill signed in 2022 required it. Long-term English learners are students who have been enrolled in U.S. schools for six years or more but have not advanced on the English proficiency test in two or more years. The state also released data for those “at risk of becoming long-term English learners,” defined as students who have been enrolled for four or five years and scored at intermediate level or below on the English proficiency test.
In the past, California had separated achievement data for English learners by those who had been enrolled for less than or more than a year, but not for long-term English learners or those at risk of becoming long-term English learners.
As a whole, students classified as English learners tend to do poorly on academic tests precisely because they are still learning English, and once they are reclassified, they tend to do much better.
Yet the data shows that long-term English learners do worse than their counterparts who have been enrolled in U.S. schools for fewer years.
Only 5.4% of long-term English learners met or exceeded English language arts standards in 2022-23, compared with 10.9% of English learners as a whole. In math, only 2.1% of long-term English learners met or exceeded the standards, versus 9.9% of English learners as a whole.
“There’s something really tragic that happens when students are not getting what they need every year, and they’re not feeling successful, and it really shapes their identity as a student,” said Nicole Knight, executive director of English language learner and multilingual achievement at Oakland Unified School District.
Knight said Oakland Unified has been separating the district’s own achievement data by the number of years English learners have been in school and found similar results. “The longer they’re in the system as long-term English learners, at least from a statistical standpoint, they tend to do worse and worse,” she said.
Conor P. Williams, senior fellow at The Century Foundation, said the data is not surprising and is likely due to several factors.
In part, these scores may have to do with the way the state defines English learners. Students who do not do well on academic tests continue to be classified as English learners because California requires students to do as well as their English-speaking peers on English language arts tests, in addition to passing the English Language Proficiency Assessment, in order to be reclassified as fluent.
“The fact that long-term English learners do particularly worse on a lot of academic metrics likely reflects the fact that there is an academic indicator in California’s reclassification criteria. That is not standard in all states,” said Williams. In many states, he said, students only have to pass an English language proficiency test in order to be reclassified as fluent.
Shelly Spiegel-Coleman, strategic adviser of Californians Together, said it’s important to note that most English learners do reclassify within six years. She said long-term English learners may not have received strong English language development support in their early years and probably no instruction in their home languages. She added that some English learners with fewer years of enrollment in U.S. schools may have arrived in the country already knowing how to read in their home languages.
A study by Californians Together showed that more than a third of long-term English learners also have disabilities that qualify them for special education services.
“Sometimes that is an excuse for folks, but those students can also reclassify, (though) it may take them a little more time,” said Knight. She said English learners with disabilities are less likely to receive quality instruction in English language development and quality special education services. “That’s a big issue that districts and schools need a lot more support and guidance with than what we currently have.”
Knight added that being classified as English learners for many years can hurt students’ self-esteem and cause them to become disengaged with school and stop turning in assignments or attending class.
The data is a call to action for districts, said Spiegel-Coleman. She said beginning next year, districts will have to include plans for long-term English learners in their local control accountability plans, or LCAPs. These are plans that every district and charter school must write every year, explaining how they will use state funds to improve educational outcomes for certain groups of students.
“When they’re writing their LCAPs, they need to look at those kids and say what is it we need to do for them?,” Spiegel-Coleman said. “Now that will happen. It will heighten their visibility, for sure.”
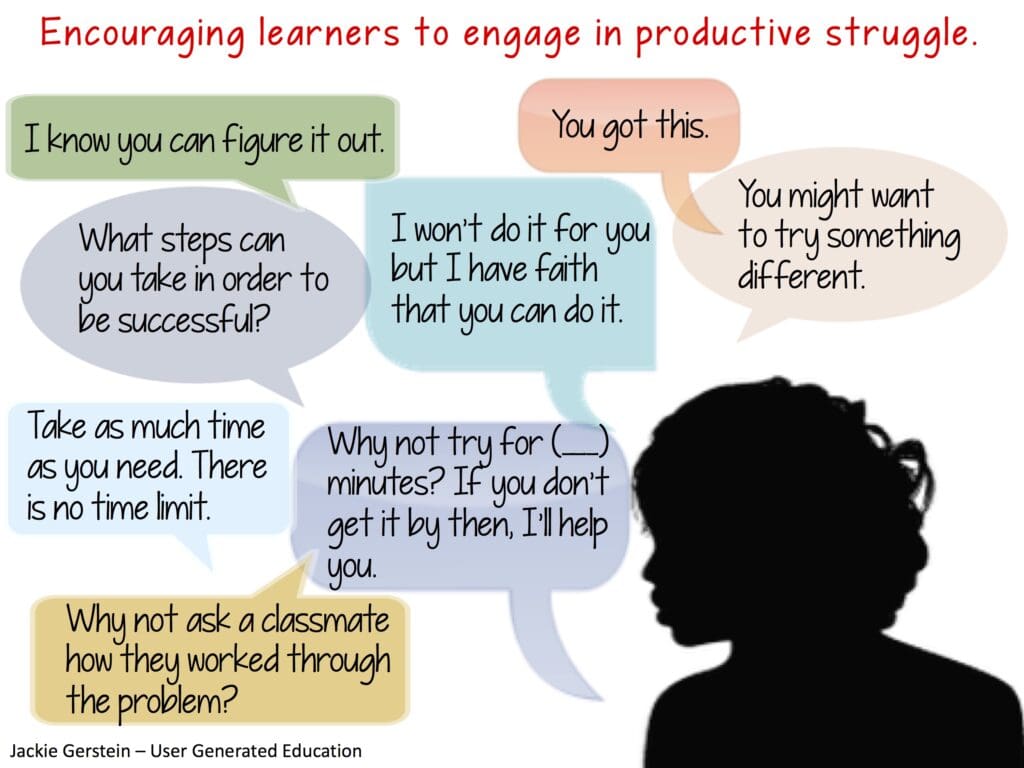
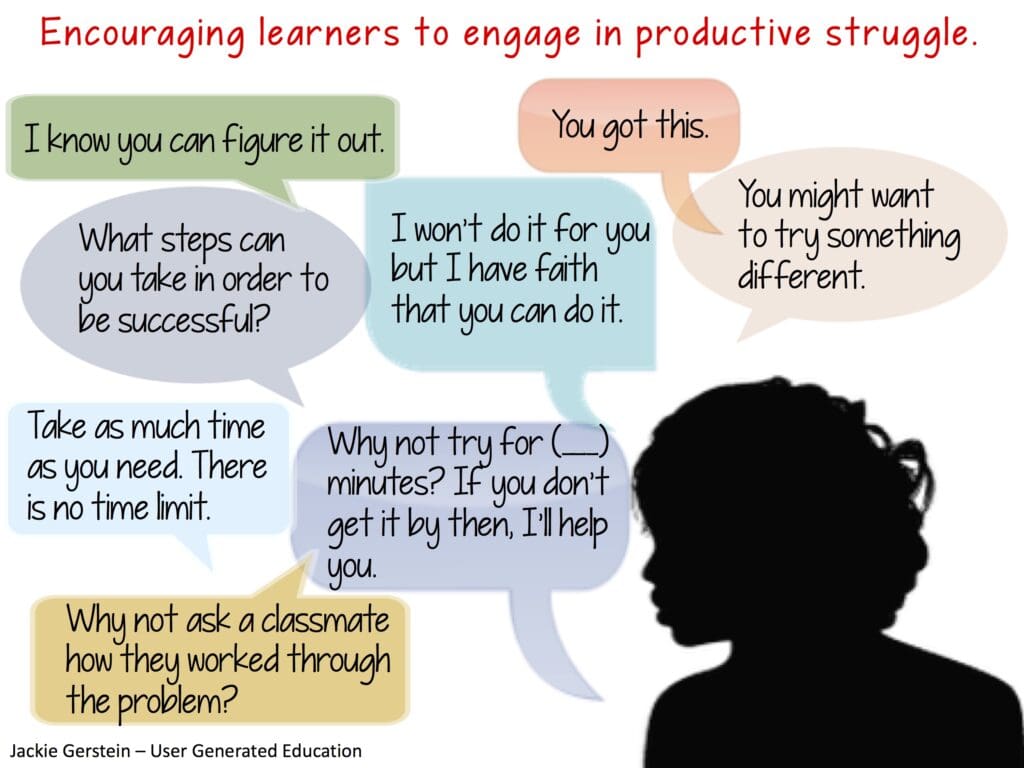
Knight said districts also need to offer more training and support for middle and high school teachers to incorporate explicit instruction in the English language, no matter what subject they teach. For example, she said Oakland Unified has worked to train middle school math teachers on how to teach students the language they need to understand in order to figure out a math problem.
She said districts can also help long-term English learners become more engaged in school, for example with internships or career education where they can use their skills in their home language.
The data also shows districts need to do more to help students learn enough English to reclassify as fluent in their first six years of school, before they become long-term English learners, both Spiegel-Coleman and Knight said.
“The number of long-term English learners in our system is really an indictment on our system as a whole, in Oakland and outside of Oakland,” Knight said.
She said some schools in Oakland reclassify almost 30% of their English learner students every year, while other schools reclassify almost none of them.
“That tells us that it’s really about the experiences they’re getting,” Knight said. “So how do we make sure more and more of our classrooms and schools are doing what these schools that have high reclassification rates are doing?”