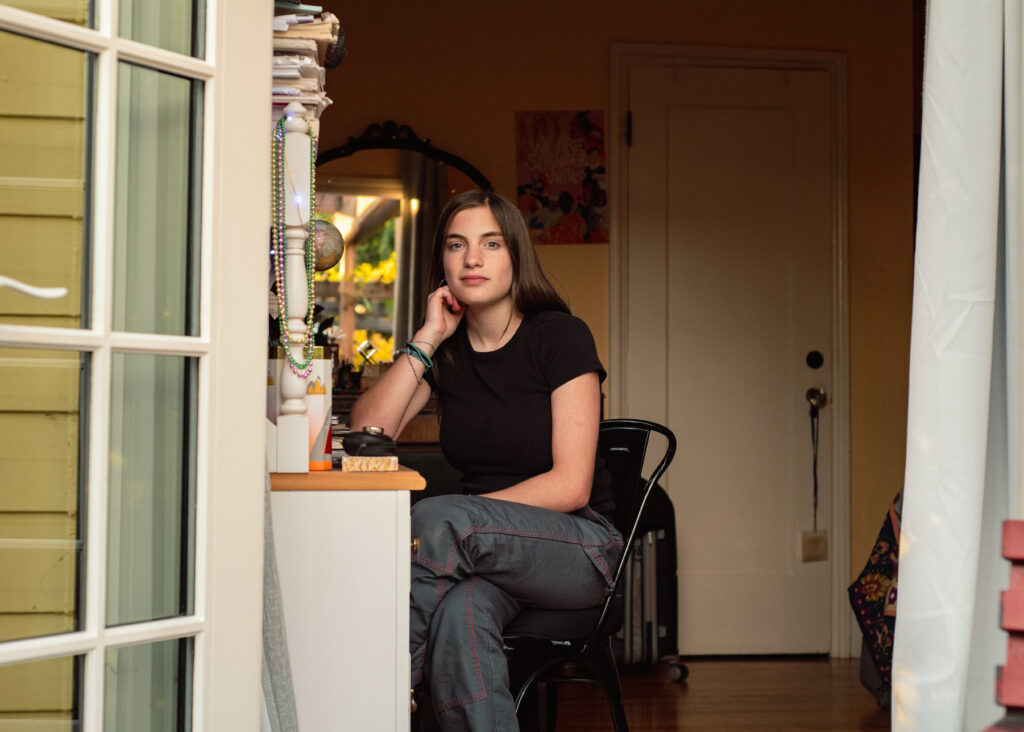Eva Levenson, now a sophomore at Berkeley High School, has struggled with dyslexia since childhood but private phonics-based intervention made a difference. “I don’t understand what’s in the way of making a shift when, both in other states and locally, districts are able to help kids now,” she recently told the school board. “How is it possible we aren’t doing it in Berkeley right now?”
Credit: Ximena Natera / Berkeleyside / CatchLight
How kids are taught to read in Berkeley is slowly starting to shift.
Teachers are studying the science of reading. More students are learning phonics, sounding out words by letters and syllables. And the school district is screening every student to flag those who may have dyslexia, a learning disorder that causes difficulty with reading, writing and spelling.
But these changes didn’t come easily. They are the result of a federal class-action lawsuit, filed in 2017, by four families of Berkeley students with dyslexia who claimed the district failed to teach them how to read.
And though the suit settled in 2021, the district’s method of teaching reading, a balanced literacy curriculum developed by Columbia University Teachers College professor Lucy Calkins called Units of Study, remains in place.
Rather than teaching students to sound out letters, the curriculum relies on a method called three-cueing — where students use context clues like pictures to figure out words — that has now been discredited and banned in several states. Some Berkeley teachers still use cueing, while others have dropped the practice.
Berkeley’s reckoning with how it teaches reading comes as California faces dismal reading scores and amid a push for the state to do more to ensure children are taught to read using evidence-based approaches. Last year, over half of California students and 33% of Berkeley students could not read at grade level.
Now, the wheels are just beginning to turn in a district long devoted to Calkins. Advocates hope that aligning with the science of reading will help close one of the largest achievement gaps in the country — last year, 26% of Black students in Berkeley schools met state standards in reading, compared with 83% of white students.
“Historically, Berkeley has been — and is — widely known for being a balanced literacy district,” Superintendent Enikia Ford Morthel said during a November panel discussion referring to the Calkins teaching method.

“What we want to be known for is being a district that is disrupting the narrative, disrupting persistent trends and data and really responding to our students,” she said. “This is not just another initiative. This truly is an imperative.”
Some students and parents aren’t yet convinced. Without a firm commitment to adopt a curriculum rooted in the science of reading, they are skeptical that they will see all the changes they believe are long overdue.
“At some point, you have to take responsibility,” said Rebecca Levenson, a parent of two children with dyslexia. Levenson wasn’t part of the lawsuit against the district, but she believes “it’s important for parents who see their children suffer to use their voice and power to make a difference for other families that are in that same situation.”
The Berkeley lawsuit was the second filed in California in 2017 over literacy instruction. In the other suit, the public-interest law firm Public Counsel charged on behalf of students in the lowest-performing schools that California had failed to meet their constitutional right to read. Under a $50 million settlement in 2020, 75 schools received funding and assistance to improve reading instruction. They were encouraged, but not mandated, to select instruction based on the science of reading.
While a district review of its elementary school literacy curriculum found that Units of Study failed to teach foundational literacy skills like phonics and vocabulary, Ford Morthel has stopped short of calling on the district to drop Lucy Calkins. The district is now beginning the process of adopting a new curriculum for the fall of 2025.
At a recent school board meeting, George Ellis, the court-appointed monitor, hammered home the importance of changing the Calkins curriculum. Without a “sound, comprehensive” core curriculum, he said, “it doesn’t matter what interventions we’re really providing, because we’re just filling up holes all over the place, and we’re never going to get caught up here.”
Attorneys and advocates hope the Berkeley lawsuit will spur other school districts to act faster to avoid legal action, accelerating the adoption of the science of reading in California and across the country. But Berkeley’s experience also demonstrates just how many barriers stand in the way of changing reading instruction.
Berkeley’s reading guru
When Lucy Calkins developed her approach in the 1990s, the balanced literacy teaching method was heralded as a new philosophy of education. Rather than teaching from rigid phonics textbooks, teachers introduced students to an entire library of independent books with the goal of teaching kids to love reading.
Calkins was the “guru of reading for people in Berkeley,” said Maggie Riddle, a former teacher and principal at Berkeley’s Jefferson Elementary, now called Ruth Acty. Once Calkins’ approach came to Berkeley, phonics came to be seen as a rote, old-school way of teaching, “dumbing down” instruction. “Berkeley was anti-phonics. One hundred percent,” Riddle said.
Berkeley wasn’t alone in this. Balanced literacy once enjoyed nearly universal popularity. “It was being used in every single Bay Area district,” said Deborah Jacobson, a special education attorney who brought the suit, a federal class action, against the Berkeley district seven years ago.

But the approach has fallen under fire amid a national reckoning over reading instruction, with a consensus growing that balanced literacy goes against what we know about how the brain works when learning to read.
This understanding anchors the science of reading, an approach backed by decades of exhaustive scientific research that suggests most children need systematic lessons in phonics, or how to sound out words, as well as other fundamentals, such as building knowledge and vocabulary, to learn to read. Teaching foundational reading skills especially benefits English learners. Advocates say reading is a civil right and phonics helps bring social justice to Black students.
More than half of states have passed laws requiring schools to align with research-based methods or favoring phonics. In September, Columbia University cut ties with the Reading and Writing Project that Calkins led for decades, citing the need to seek out new perspectives. Calkins herself has revised her curriculum to incorporate more explicit instruction in phonics and phonemic awareness.
A decade ago, California adopted a framework for K-12 literacy that encouraged districts to use evidence-based reading instruction, now commonly called the science of reading. But it wasn’t required, and the state didn’t push districts to adopt it.
Over the past two years, the state has taken steps toward a literacy plan but continues to leave to districts what curriculum and textbooks to use under a policy of local control. A new law passed in the summer will require that all children be screened for dyslexia and other reading disorders beginning in 2025. And by July 1, California will require teacher preparation programs to provide literacy training based on the science of reading.
Still, advocates say these changes don’t go far enough. The California Early Literacy Coalition plans to sponsor legislation that would create a comprehensive state literacy plan, mandating training in the science of reading for all teachers, not just new ones, and requiring the use of textbooks rooted in the approach.
In Berkeley, lawsuit cast a light
When Berkeley Unified was sued in 2017, Riddle said she saw it as an opportunity. She had moved up through the ranks to become head of K-8 schools and led legal negotiations for the district for two years. “Nobody ever wants the district to be sued, but it cast a light on the needs of kids in reading, especially kids with dyslexia,” Riddle said.
Not everyone saw it that way. It took five years to reach a settlement agreement, and the district’s core curriculum was a sticking point in negotiations. “The resistance was serious, but the lawsuit was serious, too,” recalled Riddle. During negotiations, the district implemented Fast Track Phonics to get phonics instruction into classrooms, but advocates criticized the decision as putting a Band-Aid on a broken system, leaving the core Calkins curriculum intact.
Berkeley signed the settlement agreement in 2021, but due to the pandemic, didn’t start working on implementation until the following year, extending the three-year plan until 2025. Initially, Ellis, the court monitor, criticized the school district and its board for failing to embrace the settlement. And in February, Jacobson said the district had breached the settlement agreement by moving too slowly, but decided not to file a notice in court after district leaders promised action.
In the last year and a half, the district has started taking steps toward the science of reading.
Elementary teachers did a book study of “Shifting the Balance,” an introduction to science of reading practices. The district implemented a universal screening system to flag students who might have dyslexia and started training literacy coaches to implement phonics-based intervention programs like Orton-Gillingham and Heggerty. The district also established a new department of curriculum and instruction, hired a districtwide literacy specialist, and began developing a multi-tiered system of support for struggling readers.
The district’s new focus has made a huge difference for some teachers, even those with decades of experience.
Angélica Pérez, a reading specialist at Thousand Oaks Elementary, said though she has known about phonics for years and even taught it, only recently has she received the systematic training she needed to implement it well with struggling readers.
In my 26 years in education and 15 years in the classroom, I wasn’t so aware of the importance of phonemic awareness.
Angélica Pérez, a reading specialist at Thousand Oaks Elementary in Berkeley.
The changes have won over some of the district’s critics, including Jacobson. “There is a new sense of urgency with the new administration and a new level of commitment,” Jacobson said. “Every year the light bulb seems to go on, more and more.”

They have also earned the praise of the teachers union president. “There is a systematic plan to make sure our teachers are getting what they need so they can do their jobs best,” said Matt Meyer, president of the Berkeley Federation of Teachers.
Cost to students of the lengthy legal fight
For families whose children struggle with reading, Berkeley’s decades-long commitment to balanced literacy came at a price. Many students with dyslexia have either missed out on learning, or their parents have paid thousands of dollars in private tutoring to catch them up.
“After a certain point, the research shows that it becomes unrecoverable,” said Eliza Noh, a Berkeley parent who has a child with dyslexia. “The early years for teaching people how to read are critical.”
Levenson’s two children, Eva Levenson and Wen Dolphin, both have dyslexia and attended Berkeley schools 18 years apart. But Eva received private reading intervention, while Wen did not. The family says their experience shows the difference phonics-based intervention can make.

Dolphin dropped out of school at 15, while Eva, now a sophomore at Berkeley High, is taking the same challenging classes as her peers. She began writing for The Jacket, Berkeley High’s student newspaper, and in October, penned an article about the Calkins curriculum.
“I know that my life trajectory could have been very different if I would have had the support that I needed in those really formative years,” Dolphin told a crowd at a Berkeley school board meeting last year.
When Lindsay Nofelt’s son was diagnosed with dyslexia, she shelled out thousands of dollars on a phonics-based intensive reading intervention program. Her son’s reading ability improved quickly, but what took Nofelt longer to piece together was Berkeley’s role in her son’s story.
Even after listening to Emily Hanford’s podcast “Sold a Story,” which thrust Calkins’ curriculum into the spotlight, she didn’t connect the literacy debate to Berkeley schools.
“I thought, if Emily Hanford is writing about this and sounds like it’s not serving the needs of the students, then there’s no way that Berkeley Unified school system would use such a discredited curriculum,” Nofelt said.

But over time, Nofelt realized her son wasn’t the only one in Berkeley struggling with reading. As she learned more about the science of reading and the class-action lawsuit, she realized that the kind of reading instruction Hanford was describing in her podcast was happening in Berkeley. “When I found out they were one and the same, all of the pieces fell into place,” she said.
Two years ago, Nofelt formed Reading for Berkeley to educate parents about early literacy and give them resources to advocate for their children. It’s now a resource that Nofelt wishes she had when she was trying to help her son — digestible content designed to help families ask questions about their children’s literacy education and support their reading abilities.
Today, students with dyslexia and their parents are watching Berkeley closely, their hope resting on the district’s commitment to the science of reading.
At a recent school board meeting in January, Eva Levenson told the Berkeley school board directors and superintendent that she is still waiting to see a plan that addresses the failure of the district’s core curriculum.
“I don’t understand what’s in the way of making a shift when, both in other states and locally, districts are able to help kids now. How is it possible we aren’t doing it in Berkeley right now?”