Children line up to drink water from a fountain inside Cuyama Elementary School in Santa Barbara County.
Credit: Marcio Jose Sanchez / AP Photo
It’s that time again when I line up my predictions for the year only to see events conspire to knock them down like bowling pins.
As you recall, I lay down my wager in fensters. You can, too, on a scale of 1 fenster — no way it’ll happen — to 5 – it’s bird-brain obvious (at least to you). Fensters are a cryptocurrency redeemable only in Russian rubles; currently trading at about 110 per U.S. dollar. Predict right, and you’ll be rich in no time!
2025 will be rife with conflict; you know that. It will start Jan. 20, when President Donald Trump will announce that POTUS 47 v. California will be the main attraction on his UFC fight card. Trump’s tag team of both a Republican Congress, though barely a majority, and a conservative Supreme Court will be formidable.
Since it’s often difficult to know from day to day whether Trump’s acts are grounded in personal vendettas or conservative principles, that will complicate predictions. Insiders also say his decisions change based on the last person he speaks with. Safe to say it won’t be me.
With that caution, grab your spreadsheet.
Trump’s agenda
Mass deportations could turn hundreds of thousands of kids’ lives upside down, and massive shifts in education policies could jeopardize billions of dollars in federal funding for low-income kids.
Public reaction will determine whether Trump deports tens of thousands of undocumented immigrants with criminal records or indiscriminately sends back millions of people, as he implied. Most Americans found Trump’s policy early in his first term of separating children from parent border crossers abhorrent. Scenes on social media of ICE agents’ midnight raids, leaving kids without a working parent and potentially homeless, could have the same effect. And Central Valley farmers dependent on immigrants to harvest crops will warn Trump of financial disaster; other factories dependent on immigrants to do jobs other Americans don’t want will, too.
Trump will rely on shock and awe instead: swift raids of meat-packing plants and of visible sites targeting immigrant neighborhoods in California’s sanctuary cities — to send a message: You’re not welcome here.
And it will work, as measured by fear among children, violations of habeas corpus (laws pertaining to detention and imprisonment), and, in the end, declines in illegal crossings at the border, a trend that already started, under widespread pressure, in the final year of the Biden presidency.
The likelihood that Trump’s deportations will number closer to 100,000 than a million
The likelihood that Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) will open immigrant detention centers, one each in Northern California and Southern California
The likelihood that chronic absence rates in California school districts with large undocumented immigrant populations will soar to higher than 40%
The likelihood that the number of California high school seniors in those same districts who will not fill out the federal application for college financial aid known as FAFSA because of worry about outing an undocumented parent will increase significantly
The likelihood that the Trump administration will challenge the 1981 Supreme Court decision that children present in the United States have a right to attend public school, regardless of their immigration status and that of their parents
Eliminating the U.S. Department of Education
One of the late President Jimmy Carter’s accomplishments was the creation of the Department of Education. Forty-five years later, Trump wants to dissolve it and divide responsibilities among other federal bureaucracies: Title I funding for children in poverty to the Department of Health and Human Services; federal student loans and Pell grants to the Department of Treasury. That would take congressional approval, and past efforts over the years to eliminate it — a popular Republican idea — never came close to passing.
The likelihood that Trump could get majorities in Congress to eliminate the department
With or without a department, Trump could make radical changes that could impact billions of federal education dollars for California. He could turn Title I’s $18.8 billion funding for low-income children into a block grant and let states decide how to spend it. California, which had spats with the Obama administration over how to mesh state and federal funding, might welcome that. But poor kids in other states will be at the whim of governors and legislators who won’t be held accountable.
The likelihood Trump will cut 10% to 20% from Title I funding but leave funding for special education, the Individual Disabilities Education Act, traditionally an area of bipartisan agreement, intact
The likelihood Trump will call cuts in money for Title I and the Department of Education bureaucracy a down payment for a federal K-12 voucher program
Mini-fight over state budget
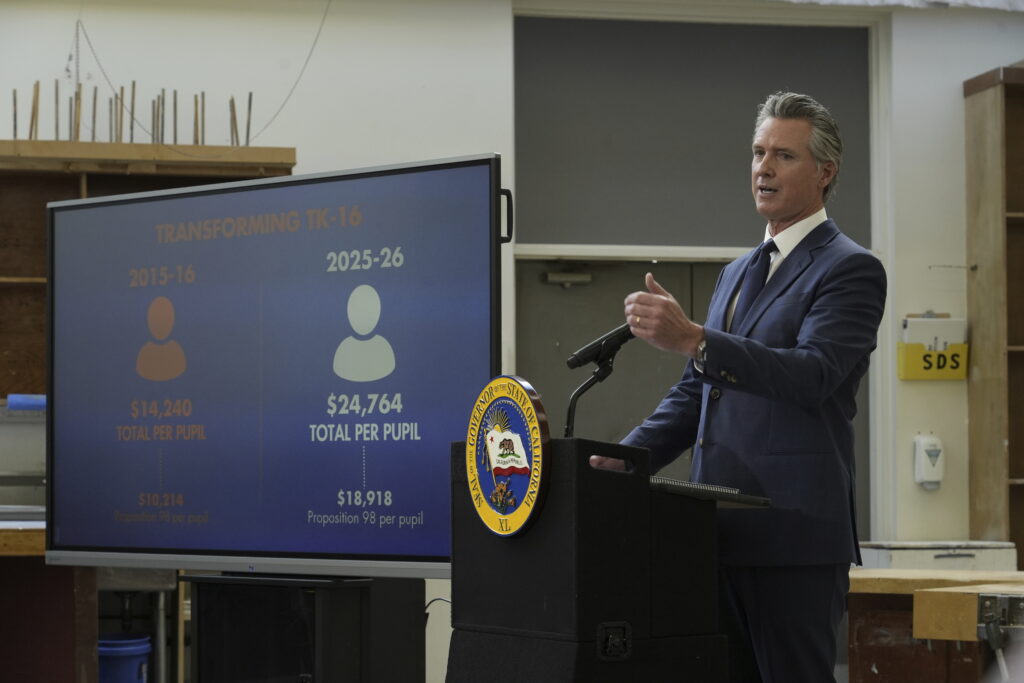
Later this week, Gov. Newsom will release his 2025-26 budget. If the Legislative Aalyst’s Office was right in its revenue projections, there will be a small cost-of-living adjustment for education programs and at least $3 billion for new spending — petty change compared with Newsom’s big initiatives for community schools and after-school programs when money flowed.
A piece of it could go toward improving math. It’s been ignored for too long.
California students perform abysmally in math: Only 31% were proficient on state tests in 2024, compared with 47% in English language arts — nothing to brag about either. In the last National Assessment of Educational Progress results, California fourth graders’ scores were behind 30 other states.
The State Board of Education approved new, ambitious math standards, amid much controversy, two years ago. The state has not jump-started statewide training for them since. But the board will adopt a new list of approved curriculum materials this summer, signaling it’s time to get rolling.
The likelihood that Newsom will include hundreds of millions of dollars for buying textbooks, training math coaches and encouraging collaboration time among teachers.
Ethnic studies tensions
Conflicts over ethnic studies, which have been simmering since the Legislature passed Assembly Bill 101 in 2021 requiring high schools to teach it will come to a head this year.
At the center of the controversy is the Liberated Ethnic Studies Model Curriculum Consortium and affiliated groups pushing an alternative version of the ethnic studies framework that the State Board of Education approved in 2021. The state framework, a guide, not a mandated curriculum, places ethnic studies in the context of an evolving American story, with a focus on struggles, progress and cultural influences of Black, Hispanic, Asian, and Native Americans.
The liberated version stresses the ongoing repression of those groups through a critique of white supremacy, capitalism and colonialism, plus, for good measure, instruction in anti-Zionism and Palestinian liberation. UC and CSU ethnic studies faculty members have led efforts to promote it, with substantial consulting contracts with several dozen districts.
AB 101’s mandate for teaching ethnic studies, starting in the fall of 2025 and requiring it for a high school diploma in 2029-30, is contingent on state funding. And that hasn’t happened, according to the Department of Finance. Meanwhile, the Legislative Jewish Caucus will reintroduce legislation to require more public disclosure before districts adopt an ethnic studies curriculum. In his Golden State Plan to Counter Antisemitism, Newsom promised to work with the caucus to strengthen AB 101 to “ensure all ethnic studies courses are free from bias, bigotry, and discriminatory content.”
Some scenarios:
The likelihood Newsom will press for amendments to AB 101 as a requirement for funding the AB 101 mandate
The likelihood that Newsom and the Legislature fund the AB 101 mandate, at least to keep it on schedule, for now
The likelihood the Jewish Caucus-led bill to strengthen transparency and AB 101’s anti-bias protections will pass with Newsom’s support
Amending the funding formula
Revising the Local Control Funding Formula, which parcels out 80% of state funding for TK-12, may get some juice this year — if not to actually amend the 12-year-old law, then at least to formally study the idea.
At an Assembly hearing last fall, the state’s leading education researchers and education advocates agreed that the landmark finance reform remains fundamentally sound, and the heart of the formula — steering more money to low-income, foster, and homeless students, as well as English learners — should be kept. However, with performance gaps stubbornly high between low-income and non-low-income students and among racial and ethnic groups, researchers also suggested significant changes to the law. The challenge is that some ideas are in conflict, and some could be expensive.
In his budgets, Gov. Gavin Newsom has directed more money to the most impoverished, low-performing schools. However, some school groups want to focus more money on raising the formula’s base funding for all students. Others want to focus attention on districts in the middle, with 35% to 55% low-income and English learners, who get less aid per student than in districts like Oakland, with higher concentrations of eligible students.
The outcome will affect how much money your school district gets, so keep an eye on what’s happening.
The likelihood that the funding formula will be amended this year
The likelihood there will be a two-year study with intent to pass legislation next year
What about tutoring?
At his preview Monday on the 2025-26 state budget, Newsom barely mentioned education. But a one-word reference to “tutoring” woke me up.
In my 2023 predictions column, I wagered three fensters that Newsom would expand a promising effort for state-driven and funded early-grades tutoring in a big way. Last year, looking back, I wrote, “It was wise advice couched as a prediction, which Gov. Newsom ignored. (It’s still a good idea.)”
So it is. Newsom created the structure for tutoring at scale when he created California College Corps. It recruits 10,000 college students and pays them $10,000 toward their college expenses in exchange for 450 community public service hours. Newsom, in setting it up, made tutoring an option. What he didn’t do is make it a priority and ask school districts, which received $6.3 billion in learning recovery money over multiple years, to make intensive, small-group “high-dosage” tutoring their priority, too. Other states, like Tennessee, have, and Maryland this year became the latest.
The likelihood that Newsom will include high-dosage tutoring in math and reading for early grades, in partnership with tutoring nonprofits, school districts, and university teacher credentialing programs
TK for all (who choose)
Starting this fall, any child who turns 4 by Sept. 1 can attend publicly funded transitional kindergarten in California. The date will mark the successful end of a four-year transition period and a $2.4 billion state investment.
“Done,” said Newsom pointing to the word stamped on a slide during a preview of the budget on Monday.
Well, not quite.
The hope of TK, the year between preschool and kindergarten, is to prepare young children for school through play and learning, thus preventing an opportunity gap from developing in a year of peak brain growth. For school districts, adding this 14th year of school offers the only hope for a source of revenue when enrollment in all grades in many districts is declining.
But in its first and initial years of full operation, TK will likely be under-enrolled statewide. There are a number of reasons. By design, the Newsom administration and Legislature are offering multiple options for parents of 4-year-olds. There are transitional kindergarten, state-funded preschools, private preschools, and state-funded vouchers for several care options, plus federal Head Start.
The state has provided financial incentives for providers to shift to serving 2- and 3-year-olds, but it will take time. The state had assumed that transitional kindergarten would draw parents attracted to classes taught by credentialed teachers in a neighborhood elementary school. Some parents prefer their preschool with an adult-child ratio of 8-to-1, instead of 12-to-1 in transitional kindergarten (a credentialed teacher and an aide in a class of up to 24) and a preschool teacher who speaks Spanish or another native language, said Bruce Fuller, a professor of education and public policy at UC Berkeley, who has been researching transitional kindergarten in California.
And many elementary schools don’t have the bigger classrooms to accommodate TK and kindergarten, or they can’t find enough credentialed teachers and aides to staff them.
In coming years, transitional kindergarten enrollment will reach closer to serving all 4-year-olds, an estimated 400,000 next year.
For now, the likelihood that transitional kindergarten will serve more than 60% of a target population
Keep on your radar
Equity in funding: Voters approved a $10 billion state construction bond, providing critical matching funding to districts that passed local bonds. But despite small fixes in Proposition 2, the first-come, first-served system favors school districts with the highest property values — whether commercial downtowns or expensive homes. The higher tax burden for low-wealth districts is why some schools are pristine and fancy, while those in neighboring districts are antiquated and decrepit. The nonprofit law firm Public Advocates threatened to file a lawsuit last fall, and hasn’t said whether it will follow through. But it would be a landmark case.
In the 1971 landmark decision in Serrano v. Priest, the California Supreme Court ruled that a school funding system tied to local property taxes violated students’ constitutional rights. Challenging the state’s reliance on districts’ disparate local property wealth to fund school facilities could be the equivalent.
Rethinking high school: Anaheim Union High School District is among the districts thinking about how the high school day could be more relevant to students’ personal and career aspirations. Anaheim Union is exploring how an expanded block schedule, team teaching, interdisciplinary courses, artificial intelligence, online learning, and job apprenticeships could transform learning.
The six-period day, education code rules in instructional minutes, and seat time may be obstacles to change and perpetuate mindsets. For now, discussions have been more conceptual than specific. The State Board of Education has a broad power to grant waivers from the state education code; State Board President Linda Darling-Hammond said the board is open to considering them. This may be the year a district or group of districts take up her offer.
Thanks for reading the column. One more toast to 2025!