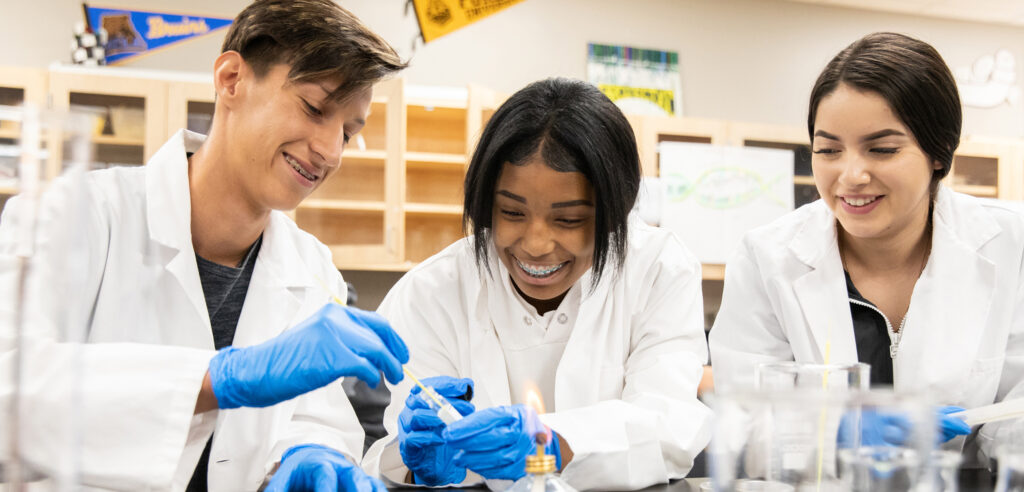
Three high school Linked Learning pathway students don lab coats as they collaborate on a hands-on science experiment, bringing classroom learning to life through real-world application.
Courtesy: Linked Learning Alliance
California’s Golden State Pathways Program is a historic commitment to career-connected learning.
In January 2025, $470 million in grants began flowing to hundreds of school communities across the state. These are huge investments, based on a proven approach to education called Linked Learning, which carefully integrates rigorous, college-bound academics with hands-on career learning experiences and strong student supports — all connected by an industry theme that meets workforce needs within the local community.
For example: In Porterville Unified School district, which serves California’s rural central valley, nearly every high school student is enrolled in a Linked Learning college and career preparatory pathway related to thriving local occupations, including those in energy, aviation, agricultural technology, and other fields. The district has an impressive 99% graduation rate, 94% of its alumni enroll in postsecondary education, and 25% percent of students earn industry-recognized certificates while still in high school. Similarly, by offering Linked Learning pathways focused on health sciences, information technology, child development and other high-growth careers, the more urban Oakland Unified School District has boosted its rates of high school graduation and completion of college-preparatory credits, and reduced absenteeism and discipline issues.
Both the extraordinary new Golden State Pathways Program (GSPP) funding and the California Master Plan for Career Education, recently released to guide educators and labor market leaders across the state, empower school leaders to build such learning pathways for their students. We wholeheartedly affirm this work.
But truly effective Linked Learning practice — the kind that extensive third-party research links to excellence and equity — requires more than working through a checklist of courses and activities. It takes intentional integration of each aspect of student experience, thoughtful measurement and supportive policy.
To this end, we offer three key recommendations:
1. District leaders should push for true college and career integration. Rather than maintain the long-standing divide between college prep curricula and career-technical education, Golden State Pathways Program resources can be applied to make core academic subjects more engaging and useful by connecting them to themed pathways focused on the high-opportunity, high-wage careers that correspond to real workforce needs in each region. Classroom learning should sync with similarly themed sequential career-technical education courses and work-based learning, like internships and apprenticeships. Districts should engage students and families to ensure pathway options are well understood, aligned with student interests, and connected to workforce demands. As modeled in Porterville and Oakland, the right industry themes bring learning to life in very tangible ways, and they build skills and mindsets that translate to success in any field of future study or employment.
2. Researchers should inform and strengthen program implementation. Rather than wait for parents and legislators to ask, “did this pathways investment work?” participating regions should develop a robust and proactive research agenda in coordination with local communities to begin generating evidence that improves outcomes along the way. Understanding student experiences, opportunities and outcomes in pathways is essential for strengthening the program over time. Research on the conditions that return the strongest results can help spread best practices across rural, suburban and urban communities.
3. Policymakers should remove barriers to effective implementation. We cannot keep asking high schools to do everything they currently do and layer additional tasks on top of it all. State and local policies that enable waivers, flexibility, or alternatives to A–G requirements for UC/CSU admissions would increase time and space in students’ schedules to engage in work-based learning. Policymakers should also build in incentives for collaboration and coordination between K–12 and postsecondary institutions to enable purposeful dual-enrollment opportunities that accelerate all students toward a valuable credential. To further our recommendation in point two above, policymakers should also ensure data systems that tag students in pathways to lower the barriers and costs of high-quality research on program outcomes.
Washington DC and California are moving in dramatically different directions on education. Where the nation is pulling back, we are charging ahead. We must continue to see this progress through. By acting on these recommendations, we prove a point: that government can respond in good faith to the public it serves. And we do not fail to miss the point of it all: that our future depends on getting education right for young people.
•••
Ash Vasudeva is president and CEO of ConnectED: The National Center for College and Career, an organization that partners with school, district, and community leaders to transform education through Linked Learning pathways.
Anne Stanton is president and CEO of the Linked Learning Alliance, an organization that leads the movement toward educational excellence and equity for every adolescent through high-quality college and career preparation.
Editors’ note: Anne Stanton is a member of the EdSource board of directors. EdSource maintains sole editorial control over the content of its coverage.
The opinions expressed in this commentary represent those of the author. EdSource welcomes commentaries representing diverse points of view. If you would like to submit a commentary, please review our guidelines and contact us.